The Role of Physical Therapy in Sports Injury Rehabilitation
Sports injuries affect athletes of all ages and activity levels, often disrupting performance, conditioning, and long-term physical health. Recovery requires more than rest alone, as untreated injuries can lead to movement limitations and recurring discomfort. Physical therapy plays a central role in guiding recovery by restoring strength, flexibility, and movement patterns through structured care. Understanding how rehabilitation supports healing provides valuable insight into how athletes return to activity safely and sustainably, which begins with examining how sports injuries occur and how recovery strategies are developed.
Understanding Sports Injuries
Sports injuries vary in severity and presentation, ranging from sudden trauma to gradual stress-related damage. Common injuries include ligament sprains, muscle strains, fractures, and repetitive-use conditions that develop over time. Sprains often affect joints such as ankles and knees when ligaments are overstretched, while strains involve muscle or tendon fibers that are pushed beyond their limits. Fractures typically result from high-impact contact or falls, while overuse injuries emerge from repeated stress without adequate recovery.
Each injury type presents unique challenges that require careful evaluation and structured intervention. Rehabilitation approaches differ depending on whether stability, mobility, or strength restoration is the primary concern. Targeted care helps support tissue healing while reducing the likelihood of compensatory movement patterns that may cause further strain. Physical therapy supports recovery by aligning treatment plans with the specific demands of each injury and the athlete’s activity level.
Identifying Causes of Athletic Injuries
Sports injuries often stem from a combination of physical and environmental factors. Improper movement mechanics, insufficient conditioning, muscle imbalances, and fatigue increase vulnerability during training and competition. Sudden changes in activity intensity or frequency may also contribute to injury risk. In contact sports, collisions and falls introduce additional injury potential that requires immediate assessment.
Addressing these contributing factors involves evaluating how the body moves under load and stress. Rehabilitation focuses on correcting inefficient patterns and reinforcing proper mechanics through guided exercises. Education plays an important role in helping athletes understand how training habits influence injury risk. By identifying root causes, recovery programs support safer return-to-play outcomes and long-term physical resilience.
Performing Diagnosis and Initial Assessment
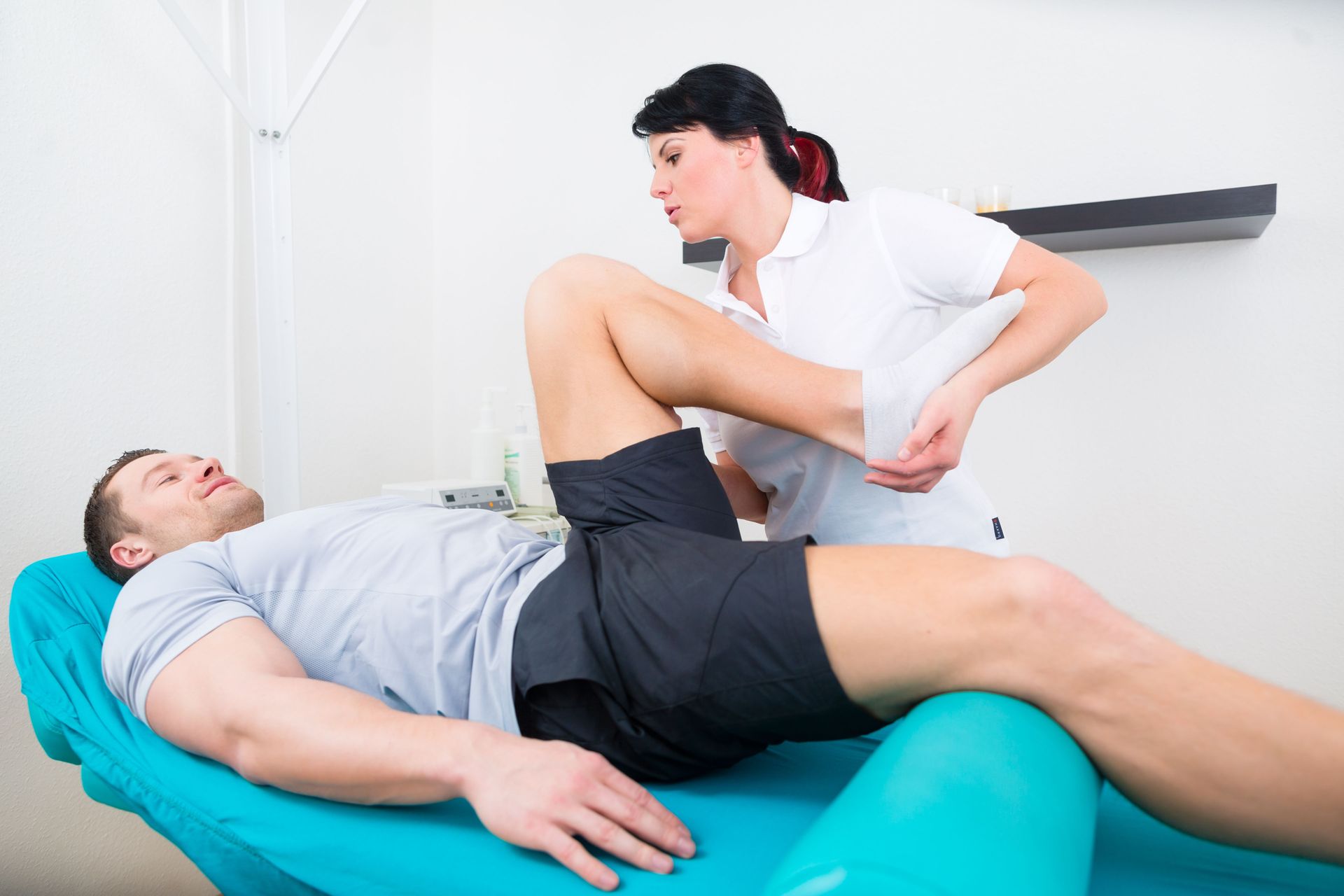
Accurate assessment establishes the foundation for effective rehabilitation. During evaluation, therapists examine the range of motion, joint stability, strength levels, and pain response. Functional movement testing helps identify limitations that may interfere with athletic tasks. Imaging studies such as X-rays or MRIs may be reviewed alongside physical findings to guide care planning.
This assessment phase allows measurable benchmarks to be established, supporting progress tracking throughout recovery. Early-stage physical therapy interventions often help reduce discomfort and restore movement before advancing to strengthening activities. Education provided during assessment helps athletes understand their condition and participate actively in their rehabilitation process.
Examining Impact on Athletic Performance
Injuries influence both immediate performance and long-term athletic capacity. Missed training sessions disrupt conditioning and skill development, while unresolved injuries may limit strength or mobility permanently. Physical limitations can alter biomechanics, increasing strain on unaffected areas of the body. Addressing injuries promptly helps prevent performance decline and secondary complications.
Rehabilitation emphasizes restoring functional movement required for sport-specific demands. Strengthening, balance training, and neuromuscular control exercises support coordinated movement under stress. Physical therapy contributes to rebuilding confidence by helping athletes regain trust in their body’s capabilities during progressive activity reintroduction.
Addressing Emotional and Psychological Effects
Injury recovery extends beyond physical healing. Athletes often experience frustration, stress, or anxiety when unable to participate in training or competition. These emotional responses may affect motivation and adherence to rehabilitation plans. Addressing mental well-being is an important component of comprehensive recovery.
Structured rehabilitation provides routine and measurable progress, which helps restore confidence. Encouragement, goal setting, and consistent communication support emotional resilience during recovery. Physical therapy environments that acknowledge psychological challenges contribute to more complete rehabilitation outcomes.
Explaining Principles of Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation programs are guided by principles focused on restoring movement efficiency, reducing discomfort, and improving overall function. Treatment plans are individualized, accounting for injury severity, activity goals, and physical conditioning. Evidence-based approaches guide progression from early recovery to functional performance.
A core element of physical therapy involves supporting the body’s natural healing processes while minimizing unnecessary stress. Active participation is encouraged through guided exercises and education. Progress monitoring allows adjustments that keep recovery aligned with functional goals and activity demands.
Defining the Role of the Physical Therapist
Physical therapists evaluate movement patterns and design care plans that address injury-related limitations. Their role includes assessing strength, flexibility, coordination, and balance to determine appropriate interventions. Treatment strategies are adjusted as recovery milestones are achieved.
Education remains central to care delivery, helping individuals understand how movement mechanics influence healing. Communication with healthcare providers supports coordinated recovery planning. According to Nova One Advisor, orthopedic-focused rehabilitation accounted for over 58% of industry share in 2023, reinforcing the importance of structured care in musculoskeletal recovery.
Applying Common Physical Therapy Techniques
Rehabilitation programs incorporate a variety of techniques to support healing. Manual therapy methods may be used to improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tension. Therapeutic exercises focus on restoring strength, endurance, and coordination. Each exercise progression aligns with healing timelines and functional goals.
Modalities such as temperature-based treatments and neuromuscular stimulation may assist with pain management and muscle activation. These approaches complement exercise-based interventions, supporting comfort and movement quality during recovery. Physical therapy integrates these techniques to address both symptom management and functional restoration.
Utilizing Tools and Equipment in Therapy
Rehabilitation settings utilize equipment designed to support safe movement progression. Resistance bands and balance tools help build strength and coordination. Stability devices support core engagement and joint control. Equipment selection reflects the recovery stage and individual capability.
Advanced technologies may assist with pain relief and neuromuscular re-education. Gait training tools and controlled treadmills support walking mechanics as recovery advances. Physical therapy environments combine traditional tools with modern equipment to support efficient and adaptable care delivery.
Coordinating With Other Healthcare Professionals
Effective rehabilitation often involves collaboration among medical providers. Coordination with physicians and orthopedic professionals ensures alignment between medical findings and rehabilitation goals. Communication supports safe progression through recovery stages.
Collaboration also helps address emotional and physical readiness for return to activity. Consistent information sharing promotes continuity of care. Physical therapy serves as a central component within this coordinated approach, bridging recovery and functional reintegration.
Managing Acute Injuries Effectively
Early-stage injury management focuses on controlling inflammation and protecting injured tissues. Activity modification, gentle movement, and education help establish safe recovery conditions. Monitoring symptoms during this phase supports timely adjustments to care strategies.
Early physical therapy involvement encourages appropriate movement while minimizing stiffness. Guidance during acute recovery supports comfort and confidence while laying the groundwork for later strengthening and conditioning efforts.
Restoring Strength and Conditioning
As healing progresses, rehabilitation emphasizes rebuilding strength and endurance. Progressive resistance exercises target affected muscle groups while supporting overall movement efficiency. Conditioning programs are adapted to sport-specific demands as recovery advances.
Therapists monitor technique and fatigue to ensure exercises remain safe and effective. Strength restoration helps reduce reinjury risk and supports long-term athletic participation. Physical therapy guides this progression with structured oversight.
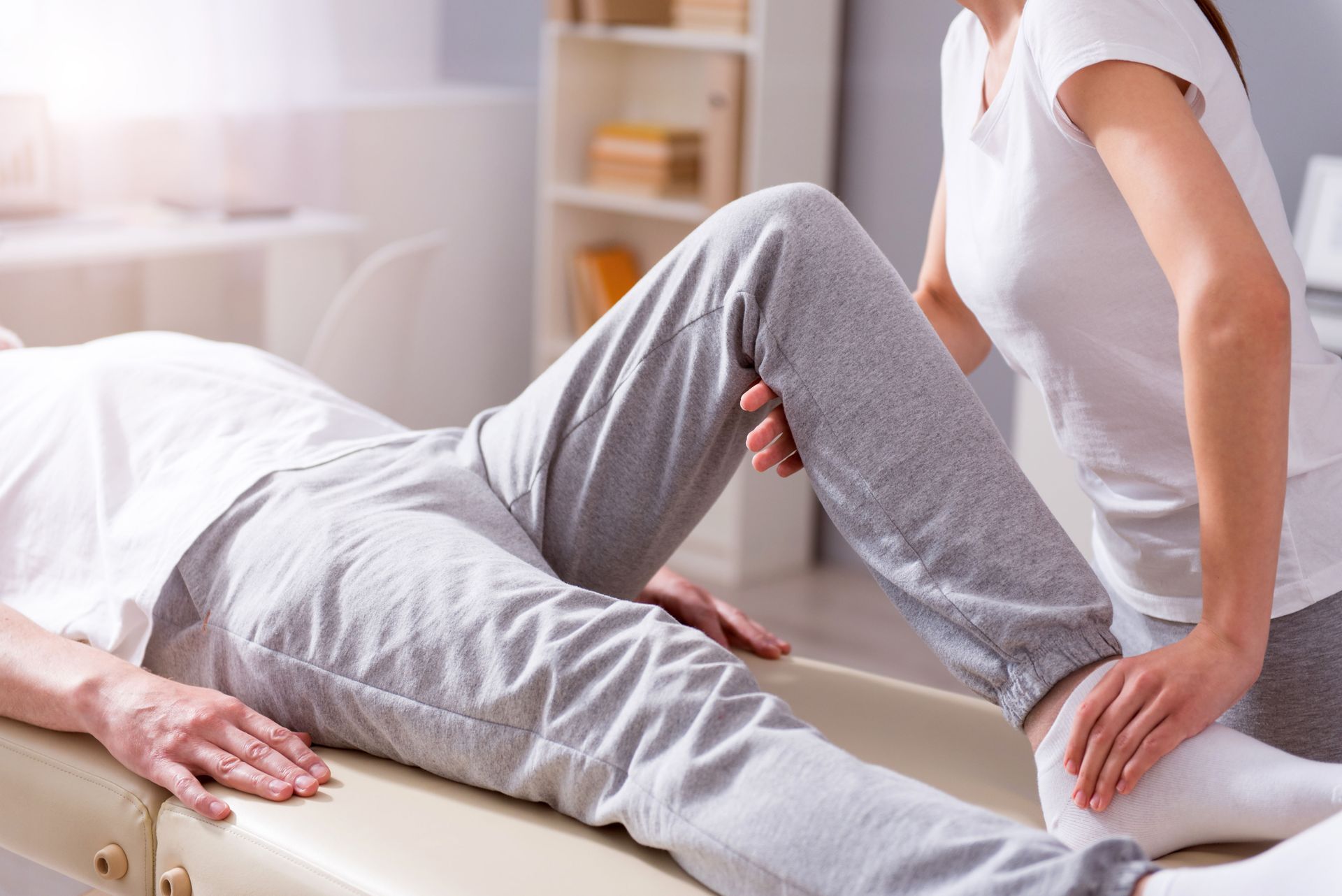
Improving Flexibility and Range of Motion
Flexibility and joint mobility remain critical throughout recovery. Stretching interventions help restore tissue elasticity and movement efficiency. Manual techniques may support joint mobility where restrictions exist.
Maintaining an appropriate range of motion supports proper biomechanics during athletic activity. Regular flexibility training reduces stiffness and supports long-term movement quality. Physical therapy integrates these strategies into comprehensive recovery planning.
Rehabilitation supports athletes beyond injury resolution by promoting sustainable movement habits and physical awareness. Recovery programs emphasize gradual reintegration into activity while reinforcing proper mechanics and conditioning strategies. Ongoing care supports long-term mobility and performance stability.
At Mobile Rehab Physical & Occupational Therapy, we deliver in-home rehabilitation that supports recovery where patients are most comfortable. Our team focuses on movement restoration, strength development, and functional progress through personalized care. Contact us today to learn how our physical therapy services support recovery and help individuals return to active living with confidence.















Share On: